Gas Turbine
Introduction
In a world rapidly transitioning towards sustainable and efficient energy sources, gas turbines have emerged as a powerful player. These innovative machines harness the potential of combustion to drive various applications, from electricity generation to aviation. This article delves into the fascinating realm of gas turbines, uncovering their inner workings, applications, and environmental impact.
Gas Turbine
Gas Turbine , A turbine is a specialized rotating engine that has the ability to extract and produce the desired energy from a fluid.
Gases, steam and water turbines usually have a protective cover around their blades that is responsible for fluid control. Covers and blades can have different geometric shapes, each of which has differences depending on the type of turbine and its application or the type of fluid and efficiency.
Todays, technology is called mother technology, and a country that can design and build gas turbines can produce anything else. Kian turbo tec is one of the best company that Providing services for gas turbines.
Solar Taurus , Solar Turbines service are comprised of Solar Turbine parts, gas turbine overhaul , field service, flexible service agreements, digital solutions. and technical training in addition to remote web based monitoring and predictive diagnostic capabilities.
Advantages of gas turbines Power to weight ratio:
Gas turbines are smaller than reciprocating engines with the same power. Gas turbines are one of the power generation machines that are widely used today in various industries such as power plants, refineries, petrochemicals and oil and gas industries.
How Do Gas Turbines Work?
A gas turbine consists of three main parts: the compressor, the combustor, and the turbine. The compressor draws in air and compresses it. The compressed air is then mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustor. The hot gases from the combustor expand and drive the turbine. The turbine shaft is connected to a generator, which produces electricity.
Types of gas turbines
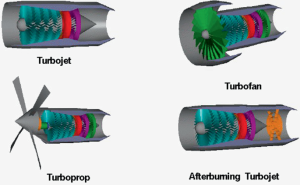
Turbojet
A turbojet is a type of jet engine in which all of the air that enters the engine is passed through the combustion process, and the exhaust gases are expelled through a nozzle to create thrust.
How It Works?
-
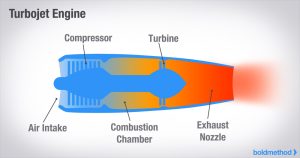
- Air enters through the intake and is compressed by a compressor.
- The compressed air is mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber.
- The resulting high-speed exhaust gases pass through a turbine (which drives the compressor) and are expelled through a nozzle to produce thrust.
Turbofan
A turbofan is a type of jet engine that has a big fan at the front.This fan helps the engine produce more thrust by pushing some of the air around the engine, instead of sending it all through the core. This is called a bypass engine.Companies like Kianturbotec design and make these kinds of engines,which are used in most modern airplanes because they are more efficient and quieter.
How It Works?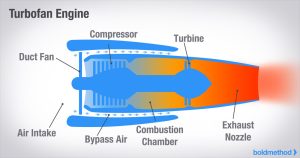
-
- Air is drawn in by a large fan at the front.
- A portion of this air is directed into the core of the engine, where it goes through a similar process as in a turbojet (compression, combustion, turbine, and exhaust).
- The rest of the air bypasses the core and is accelerated by the fan to provide additional thrust, which is more efficient at lower speeds.
Turboprop
turboprop engine is a type of jet engine that uses a gas turbine to drive a propeller.It works by using the turbine to spin the propeller,which creates thrust.
Here’s how it works in simpler terms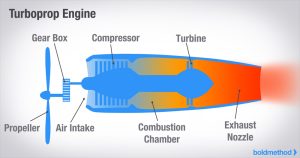
- Air Intake: Air enters the engine and is compressed.
- Compression and Combustion: The compressed air is mixed with fuel and ignited in the combustion chamber.
- Turbine: The hot gases flow through a turbine, which powers the propeller.
- Propeller: The turbine drives a large propeller attached to the engine, which generates thrust.
Afterburning Turbojet(Afterburner)
An Afterburning Turbojet, or afterburner, is a type of gas turbine engine designed to increase thrust by injecting additional fuel into the exhaust gases after they have passed through the combustion chamber and turbine.
The afterburner ignites this extra fuel, causing a further rise in temperature and volume, which results in a significant boost in thrust. This process is particularly useful for supersonic speeds, where maximum thrust is required for rapid acceleration and maneuverability. While afterburners offer increased power, they are less fuel-efficient, as they burn extra fuel solely to enhance performance.
Afterburning turbojets are primarily found in military fighter jets and supersonic aircraft,such as the F-16 Fighting Falcon and Concorde.

concorde

flighter jet-F16
Kianturbotec and some other companies like that specialize in the development and production of advanced afterburning turbojet engines,focusing on maximizing thrust output for high-speed applications while ensuring engine reliability and durability under extreme conditions.
Applications of Gas Turbines
Gas turbines are used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Power generation: Gas turbines are used to generate electricity in power plants. They are also used in combined cycle power plants, which can be more efficient than simple cycle gas turbines.
Aircraft propulsion: Gas turbines are used to power jet engines. They are also used in some helicopter engines.
Ship propulsion: Gas turbines are used to power ships. They are also used in some locomotives.
Other applications: Gas turbines are also used in a variety of other applications, such as pumping oil and gas, and manufacturing fertilizer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gas Turbines.
Disadvantages of Gas Turbines:
Gas turbines also have some disadvantages, including:
High cost: Gas turbines can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
Noise: Gas turbines can be noisy, especially during startup and shutdown.
Fuel consumption: Gas turbines can consume a lot of fuel, especially when operating at high loads.
Comparison of Simple Cycle and Combined Cycle Gas Turbines
| Characteristic | Simple Cycle Gas Turbine | Combined Cycle Gas Turbine |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 30-40% | 50-60% |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Emissions | Higher | Lower |
| Noise | Louder | Quieter |
Applications of Gas Turbines
| Application | Percentage of Gas Turbines Used |
|---|---|
| Power generation | 60% |
| Aircraft propulsion | 20% |
| Ship propulsion | 10% |
| Other applications | 10% |
Recent Advances and Future Trends
- Hybrid Systems: Combining gas turbines with renewable energy systems, such as solar or wind, can improve efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
- High-Efficiency Gas Turbines: Manufacturers are working on producing next-generation gas turbines that operate at even higher temperatures and efficiencies, using advanced materials like ceramics and superalloys.
- Zero-Carbon Fuels: The shift to hydrogen and biofuels in gas turbines could make them more environmentally friendly,as these fuels have lower or zero carbon emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Gas Turbine for power production
Gas Turbine Components , The increasing use of gas turbines in various industries, especially in the oil and electronics industries. such as moving large pumps inside oil and gas pipelines. supplying energy required by factories and special areas away from the network is very significant and significant. . Also in the power generation industry, global grids are very popular as units that can be put into orbit quickly.
Gas turbine
is a type of internal combustion engine of rotating equipment machines. which operates based on the energies of gases produced from the combustion of various fuels. It is mainly used in fossil fuel power plants. but in helicopter engines, engines of some passenger planes. engines of fighter planes and turbine engines of some types of ships, versions of gas turbines are also used.
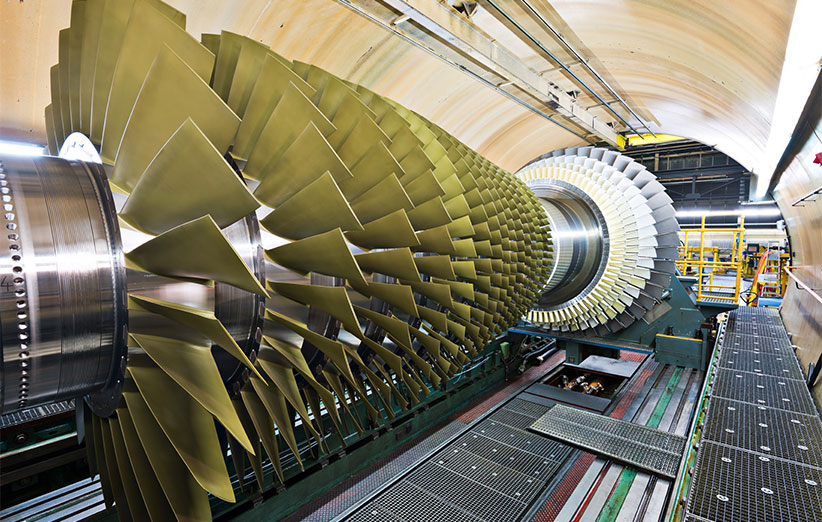


Gas turbines, often referred to as combustion turbines, are mechanical devices that convert energy from fuel into mechanical motion. This motion powers various applications, making gas turbines indispensable in today’s energy landscape. Operating on the Brayton cycle, gas turbines consist of three main components: the compressor section, the combustion chamber, and the turbine section.

Solar gas turbine , Among renewable energies, the sun, as an endless source of energy, has always been in the focus of researchers. The use of solar radiation energy in conventional power generation systems. such as gas turbines can play an important role in reducing fuel consumption and environmental pollution. On the other hand, this issue increases the efficiency of the desired cycles and improves their performance.
Gas turbine components
are in fact a rotating internal combustion engine from the family of turbomachines, which is known in the public mind as the most widely used aircraft jet engine. The Gas Turbine Efficiency works by igniting the difference between compressed air and fuel and passing the product through a series of rotating disks of the turbine, which causes the rotational power of a shaft or creates a driving reaction force or a combination of these two phenomena.
Kian turbo tec Gas Turbines
Gas Turbines Service Companies, Each gas turbine efficiency has a compressor to compress the air. a combustion chamber to mix the fuel with the air and its combustion. and a turbine to convert the internal energies of the hot, high-pressure gases into mechanical energy.
Part of the mechanical energy generated by the turbine is used to turn the compressor of the gas turbine compressor. and the rest of the energy produced, depending on the intended use for the gas turbines, may cause the electric generator to rotate.
Gas Engine
Kian Turbo Tec offers a competitive alternative for gas turbine owners and operators in the overhaul of rotors. Dedicated rotor overhaul engineers offering knowledgeable advice. experience of commercial operation. and an ex-stock supply of necessary components and rotating parts.
Gas Turbine Overhaul and Kian Turbo Tec offers a competitive alternative for gas turbine owners and operators in the overhaul of rotors. Dedicated rotor overhaul engineers offering knowledgeable advice. experience of commercial operation.
Conclusion
Gas turbines are a versatile and efficient type of engine that is used in a wide variety of applications. They are a key part of the global energy infrastructure and are likely to continue to be used for many years to come.